
Lady Nijō
Lady Nijō (後深草院二条 Go-Fukakusain no Nijō) (1258 – after 1307) was a Japanese historical figure. She was a concubine of Emperor Go-Fukakusa from 1271 to 1283, and later became a Buddhist nun. After years of travelling, around 1304-7 she wrote an autobiographical novel, Towazugatari (literally "An Unasked-For Tale", commonly translated into English as The Confessions of Lady Nijō), the work for which she is known today, and which is also the only substantial source of information on her life.
Lady Nijō was a member of the powerful Fujiwara Nijō Family. Her father and paternal grandfather held important positions at the imperial court, and many of her relatives and ancestors had high reputations for their literary abilities. Her real name does n
If you like author Lady Nijō here is the list of authors you may also like
Buy books on AmazonTotal similar authors (25)
-

Murasaki Shikibu
Murasaki Shikibu (Japanese: 紫式部), born around 978 in Heian-kyō (modern-day Kyoto), is widely celebrated as one of the most important and pioneering figures in Japanese literature. Though her real name is not definitively known, she is remembered by the sobriquet “Murasaki Shikibu,” a name derived from a combination of her most famous literary character, Murasaki, and her father’s official court position in the Bureau of Ceremonial (Shikibu-shō). This alias reflects both her literary contribution and her aristocratic lineage.
Buy books on Amazon
She was born into the prestigious Fujiwara family, though to a lesser branch that did not hold the most powerful positions in court. Her father, Fujiwara no Tametoki, was a scholar, poet, and provincial governor. Recogni -

Kenji Miyazawa
His name is written as 宮沢賢治 in Japanese, and translated as 宮澤賢治 in Traditional Chinese.
Buy books on Amazon
Kenji Miyazawa (1896-1933) was born in Iwate, one of the northernmost prefectures in Japan. In high school, he studied Zen Buddhism and developed a lifelong devotion to the Lotus Sutra, a major influence on his writing. After graduating from an agricultural college, he moved to Tokyo to begin his writing career but had to return home to care for a sick sister. He remained in his home in Iwate for the rest of his life. One of his best-known works is the novel Night on the Galactic Railroad, which was adapted into anime in the late twentieth century, as were many of his short stories. Much of his poetry is still popular in Japan today. -

Saikaku Ihara
Saikaku Ihara (井原 西鶴) was a Japanese poet and creator of the "floating world" genre of Japanese prose (ukiyo-zōshi).
Buy books on Amazon
Born the son of the wealthy merchant Hirayama Tōgo (平山藤五) in Osaka, he first studied haikai poetry under Matsunaga Teitoku, and later studied under Nishiyama Sōin of the Danrin School of poetry, which emphasized comic linked verse. Scholars have described numerous extraordinary feats of solo haikai composition at one sitting; most famously, over the course of a single day and night in 1677, Saikaku is reported to have composed at least 16,000 haikai stanzas, with some rumors placing the number at over 23,500 stanzas.
Later in life he began writing racy accounts of the financial and amorous affairs of the merchant class and the -

Thomas Boyd
Thomas Boyd was raised by his mother's family due to his father's death before he was born. While still in school, he and a friend enlisted in the US Marine Corps and saw service in France, where he was gassed in 1918.
Buy books on Amazon
Upon discharge from the occupation forces in 1919, Boyd tried several occupations before becoming a writer for newspapers in Minneapolis and St. Paul, Minnesota. He opened a bookstore, Kilmarnock Books, in St. Paul, which became the locus of literary figures, including Sinclair Lewis. He was urged to write and produced the 1923 novel, Through the Wheat, based in part on his own war experiences.
Boyd later remarried and became interested in Socialist causes during the Depression, eventually running as the Communist candidate for -

Murasaki Shikibu
Murasaki Shikibu (Japanese: 紫式部), born around 978 in Heian-kyō (modern-day Kyoto), is widely celebrated as one of the most important and pioneering figures in Japanese literature. Though her real name is not definitively known, she is remembered by the sobriquet “Murasaki Shikibu,” a name derived from a combination of her most famous literary character, Murasaki, and her father’s official court position in the Bureau of Ceremonial (Shikibu-shō). This alias reflects both her literary contribution and her aristocratic lineage.
Buy books on Amazon
She was born into the prestigious Fujiwara family, though to a lesser branch that did not hold the most powerful positions in court. Her father, Fujiwara no Tametoki, was a scholar, poet, and provincial governor. Recogni -

Émile Zola
Émile Zola was a prominent French novelist, journalist, and playwright widely regarded as a key figure in the development of literary naturalism. His work profoundly influenced both literature and society through its commitment to depicting reality with scientific objectivity and exploring the impact of environment and heredity on human behavior. Born and raised in France, Zola experienced early personal hardship following the death of his father, which deeply affected his understanding of social and economic struggles—a theme that would later permeate his writings.
Buy books on Amazon
Zola began his literary career working as a clerk for a publishing house, where he developed his skills and cultivated a passion for literature. His early novels, such as Thérèse -

Virginia Woolf
(Adeline) Virginia Woolf was an English novelist and essayist regarded as one of the foremost modernist literary figures of the twentieth century.
Buy books on Amazon
During the interwar period, Woolf was a significant figure in London literary society and a member of the Bloomsbury Group. Her most famous works include the novels Mrs. Dalloway (1925), To the Lighthouse (1927), and Orlando (1928), and the book-length essay A Room of One's Own (1929) with its famous dictum, "a woman must have money and a room of her own if she is to write fiction." -

Yasunari Kawabata
Yasunari Kawabata (川端 康成) was a Japanese short story writer and novelist whose spare, lyrical, subtly-shaded prose works won him the Nobel Prize for Literature in 1968, the first Japanese author to receive the award. His works have enjoyed broad international appeal and are still widely read today.
Buy books on Amazon
Nobel Lecture: 1968
http://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prize... -
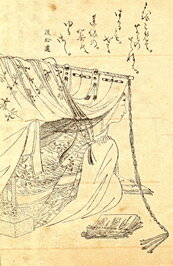
Sei Shōnagon
清少納言 in Japanese
Buy books on Amazon
Sei Shonagon (c. 966 -1017) was a Japanese author and a court lady who served the Empress Teishi (Sadako) around the year 1000 during the middle Heian period. She is best known as the author of "The Pillow Book" (枕草子 makura no sōshi). -

Evelyn Waugh
Evelyn Waugh's father Arthur was a noted editor and publisher. His only sibling Alec also became a writer of note. In fact, his book “The Loom of Youth” (1917) a novel about his old boarding school Sherborne caused Evelyn to be expelled from there and placed at Lancing College. He said of his time there, “…the whole of English education when I was brought up was to produce prose writers; it was all we were taught, really.” He went on to Hertford College, Oxford, where he read History. When asked if he took up any sports there he quipped, “I drank for Hertford.”
Buy books on Amazon
In 1924 Waugh left Oxford without taking his degree. After inglorious stints as a school teacher (he was dismissed for trying to seduce a school matron and/or inebriation), an appren -

Natsuo Kirino
NATSUO KIRINO (桐野夏生), born in 1951 in Kanazawa (Ishikawa Prefecture) was an active and spirited child brought up between her two brothers, one being six years older and the other five years younger than her. Kirino's father, being an architect, took the family to many cities, and Kirino spent her youth in Sendai, Sapporo, and finally settled in Tokyo when she was fourteen, which is where she has been residing since. Kirino showed glimpses of her talent as a writer in her early stages—she was a child with great deal of curiosity, and also a child who could completely immerse herself in her own unique world of imagination.
Buy books on Amazon
After completing her law degree, Kirino worked in various fields before becoming a fictional writer; including scheduling -

Marcel Schwob
Marcel Schwob (1867-1905) was one of the key symbolist writers, standing in French literature alongside such names as Stephane Mallarme, Octave Mirbeau, Andre Gide, Leon Bloy, Jules Renard, Remy de Gourmont, and Alfred Jarry. His best-known works are Double Heart (1891), The King In The Gold Mask (1892), and Imaginary Lives (1896).
Buy books on Amazon -

Tove Jansson
Tove Jansson was born and died in Helsinki, Finland. As a Finnish citizen whose mother tongue was Swedish, she was part of the Swedish-speaking Finns minority. Thus, all her books were originally written in Swedish.
Buy books on Amazon
Although known first and foremost as an author, Tove Jansson considered her careers as author and painter to be of equal importance.
Tove Jansson wrote and illustrated her first Moomin book, The Moomins and the Great Flood (1945), during World War II. She said later that the war had depressed her, and she had wanted to write something naive and innocent. Besides the Moomin novels and short stories, Tove Jansson also wrote and illustrated four original and highly popular picture books.
Jansson's Moomin books have been translated in -

Seichō Matsumoto
Seicho Matsumoto (松本清張, Matsumoto Seichō), December 21, 1909 – August 4, 1992) was a Japanese writer.
Buy books on Amazon
Matsumoto's works created a new tradition of Japanese crime fiction. Dispensing with formulaic plot devices such as puzzles, Matsumoto incorporated elements of human psychology and ordinary life into his crime fiction. In particular, his works often reflect a wider social context and postwar nihilism that expanded the scope and further darkened the atmosphere of the genre. His exposé of corruption among police officials as well as criminals was a new addition to the field. The subject of investigation was not just the crime but also the society in which the crime was committed.
The self-educated Matsumoto did not see his first book in print u -

Akira Yoshimura
Prize winning Japanese writer. Akira Yoshimura was the president of the Japanese writers union and a PEN member. He published over 20 novels, of which in particular On Parole and Shipwrecks are internationally known and have been translated into several languages. In 1984 he received the Yomiuri Prize for his novel Hagoku (破獄,engl. prison break) based on the true story of Yoshie Shiratori.
Buy books on Amazon -

Michitsuna no Haha
Michitsuna no Haha (c.935-995) was a Heian period writer in Japan. Her true name is unknown to history. The term Michitsuna no Haha literally translates to Michitsuna's mother. She is a member of the Thirty-six Medieval Poetry Immortals (中古三十六歌仙 chūko sanjurokkasen).
Buy books on Amazon
She wrote the Kagerō Nikki about her troubled marriage to Fujiwara no Kaneie, (who served as Sesshō and Kampaku,) which is a classic of Japanese literature.
(from Wikipedia) -
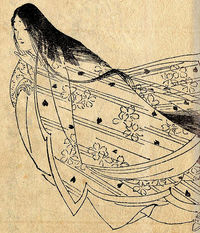
Ono no Komachi
Ono no Komachi (小野 小町?, c. 825 – c. 900) was a Japanese waka poet, one of the Rokkasen — the six best waka poets of the early Heian period. She was renowned for her unusual beauty, and Komachi is today a synonym for feminine beauty in Japan.[1] She also counts among the Thirty-six Poetry Immortals.
Buy books on Amazon -

Marguerite de Navarre
Marguerite de Navarre, also known as Marguerite d'Angoulême and Margaret of Navarre, was the queen consort of King Henry II of Navarre. As patron of humanists and reformers, and as an author in her own right, she was an outstanding figure of the French Renaissance. Samuel Putnam called her "The First Modern Woman".
Buy books on Amazon -

Tamiki Hara
Hara Tamiki was a Japanese author who survived the Hiroshima bombing by US forces in World War 2, he used that experience to influence the work he is most well known for, his atomic bomb literature.
Buy books on Amazon -

Hiromi Kawakami
Kawakami Hiromi (川上弘美 Kawakami Hiromi) born April 1, 1958, is a Japanese writer known for her off-beat fiction.
Buy books on Amazon
Born in Tokyo, Kawakami graduated from Ochanomizu Women's College in 1980. She made her debut as "Yamada Hiromi" in NW-SF No. 16, edited by Yamano Koichi and Yamada Kazuko, in 1980 with the story So-shimoku ("Diptera"), and also helped edit some early issues of NW-SF in the 1970s. She reinvented herself as a writer and wrote her first book, a collection of short stories entitled God (Kamisama) published in 1994. Her novel The Teacher's Briefcase (Sensei no kaban) is a love story between a woman in her thirties and a man in his sixties. She is also known as a literary critic and a provocative essayist.
(from Wikipedia) -

Thomas Boyd
Thomas Boyd was raised by his mother's family due to his father's death before he was born. While still in school, he and a friend enlisted in the US Marine Corps and saw service in France, where he was gassed in 1918.
Buy books on Amazon
Upon discharge from the occupation forces in 1919, Boyd tried several occupations before becoming a writer for newspapers in Minneapolis and St. Paul, Minnesota. He opened a bookstore, Kilmarnock Books, in St. Paul, which became the locus of literary figures, including Sinclair Lewis. He was urged to write and produced the 1923 novel, Through the Wheat, based in part on his own war experiences.
Boyd later remarried and became interested in Socialist causes during the Depression, eventually running as the Communist candidate for -

Cristina Campo
Cristina Campo was the pen name of Vittoria Maria Angelica Marcella Cristina Guerrini, an Italian writer and translator. During World War II, she began translating into Italian literary works by authors such as Katherine Mansfield, Eduard Mörike and Hugo von Hofmannsthal. She began translating works by Simone Weil into Italian.
Buy books on Amazon -

Andrei Platonov
Andrei Platonov, August 28, 1899 – January 5, 1951, was the pen name of Andrei Platonovich Klimentov, a Soviet author whose works anticipate existentialism. Although Platonov was a Communist, his works were banned in his own lifetime for their skeptical attitude toward collectivization and other Stalinist policies.
Buy books on Amazon
From 1918 through 1921, his most intensive period as a writer, he published dozens of poems (an anthology appeared in 1922), several stories, and hundreds of articles and essays, adopting in 1920 the Platonov pen-name by which he is best-known. With remarkably high energy and intellectual precocity he wrote confidently across a wide range of topics including literature, art, cultural life, science, philosophy, religion, education -

Saikaku Ihara
Saikaku Ihara (井原 西鶴) was a Japanese poet and creator of the "floating world" genre of Japanese prose (ukiyo-zōshi).
Buy books on Amazon
Born the son of the wealthy merchant Hirayama Tōgo (平山藤五) in Osaka, he first studied haikai poetry under Matsunaga Teitoku, and later studied under Nishiyama Sōin of the Danrin School of poetry, which emphasized comic linked verse. Scholars have described numerous extraordinary feats of solo haikai composition at one sitting; most famously, over the course of a single day and night in 1677, Saikaku is reported to have composed at least 16,000 haikai stanzas, with some rumors placing the number at over 23,500 stanzas.
Later in life he began writing racy accounts of the financial and amorous affairs of the merchant class and the -

Natsume Sōseki
Natsume Sōseki (夏目 漱石), born Natsume Kinnosuke (夏目 金之助), was a Japanese novelist. He is best known for his novels Kokoro, Botchan, I Am a Cat and his unfinished work Light and Darkness. He was also a scholar of British literature and composer of haiku, kanshi, and fairy tales. From 1984 until 2004, his portrait appeared on the front of the Japanese 1000 yen note. In Japan, he is often considered the greatest writer in modern Japanese history. He has had a profound effect on almost all important Japanese writers since.
Buy books on Amazon